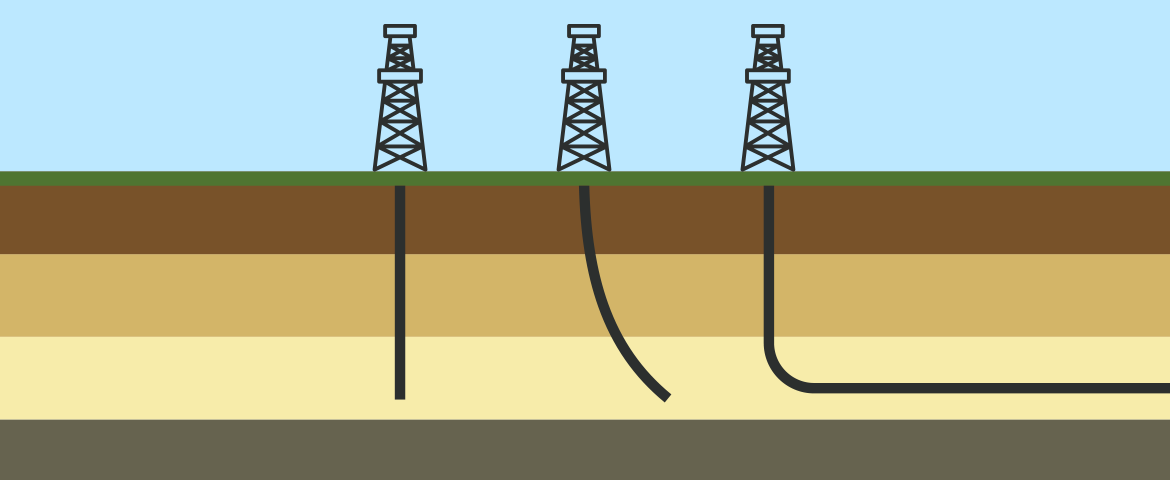
Exploring Directional Drilling: A Technique Beyond the Vertical
In the world of drilling and resource extraction, various techniques have evolved to access valuable reserves beneath the Earth’s surface. One such method that has gained attention and sometimes controversy is directional drilling. This article will delve into the concept of directional drilling, its applications, advantages, and the environmental concerns associated with it. What is slant drilling?
Understanding Directional Drilling
Directional drilling, also known as deviated drilling, is a technique that allows operators to bore wells at an angle rather than drilling vertically. This method enables access to oil, natural gas, water, or other valuable resources that may not be easily reachable with traditional vertical drilling.
How Directional Drilling Works
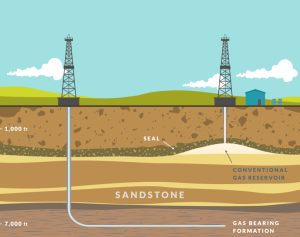
The directional drilling process involves several key components and steps:
Wellbore Design: Engineers meticulously plan the trajectory of the wellbore, considering geological formations, reservoir locations, and target depths. They use advanced computer simulations and data analysis to optimize the drilling path.
Drilling Equipment: Specialized drilling equipment, including downhole motors and rotary steerable systems, allows the drill bit to change direction as needed.
Measurement Tools: Real-time measurements are crucial in directional drilling. Tools like inclinometers and gyroscopes provide continuous data on the borehole’s orientation, helping the drillers adjust the drilling angle as required.
Mud and Fluids: Drilling fluids are pumped into the well to cool the drill bit, remove cuttings, and maintain wellbore stability. These fluids also help control pressure and prevent blowouts.
Logging and Evaluation: While drilling, operators use various logging tools to assess geological formations, locate hydrocarbons or other resources, and ensure drilling stays on course.
Completion: Once the desired depth or target is reached, the well is completed with casing and cement to ensure structural integrity and prevent contamination.
Applications of Directional Drilling
Directional drilling finds applications in several industries:
Oil and Gas Exploration: The oil and gas industry relies heavily on directional drilling to access reserves located beneath difficult terrain, such as offshore deposits or reserves located beneath populated areas.
Environmental Remediation: In situations where contamination has occurred underground, directional drilling can be used to extract or treat pollutants without disturbing the surface.
Geothermal Energy: Directional drilling is employed to tap into geothermal reservoirs, harnessing renewable energy for electricity generation and heating.
Water Resources: Directional drilling can access deep aquifers or water sources in challenging geological conditions, helping to secure freshwater supplies.
Advantages of Directional Drilling
Directional drilling offers numerous advantages over conventional vertical drilling:
Access to Remote Reserves: It allows access to resources that would otherwise be unreachable due to geological or logistical constraints.
Reduced Environmental Impact: By drilling at an angle, operators can minimize surface disturbance and environmental impact, making it an environmentally responsible option.
Cost Efficiency: Directional drilling often reduces drilling costs by optimizing well placement, minimizing the number of wells needed, and increasing resource recovery.
Enhanced Safety: It can reduce the risks associated with drilling in challenging environments or densely populated areas.
Environmental Concerns
While directional drilling offers various benefits, it is not without environmental concerns:
Subsurface Disturbance: Even though surface disruption is minimized, the subsurface can still be impacted. This can affect local ecosystems and groundwater quality.
Resource Depletion: Exploiting resources that were previously inaccessible can lead to overexploitation and depletion if not managed sustainably.
Risk of Accidents: The complexity of directional drilling introduces additional risks, such as well blowouts or equipment failures. What is slant drilling?
Conclusion
Directional drilling is a valuable technique that has revolutionized resource extraction and exploration. Its ability to access hard-to-reach reserves with reduced environmental impact and cost efficiency makes it an attractive option for various industries. However, it is essential to balance its advantages with potential environmental and safety concerns to ensure responsible resource management and minimize negative impacts on our planet. As technology continues to advance, directional drilling techniques are likely to become even more precise and environmentally friendly. https://drillitco.com.au/directional-drilling/