The Evolution of Directional Drilling
Directional drilling has revolutionized the oil and gas industry, enabling access to reserves previously deemed inaccessible. Historically, drilling was a straightforward vertical process, limited to reaching reservoirs directly below the surface. However, the evolution of directional drilling techniques has opened up new frontiers, allowing engineers to navigate through complex geological formations with precision. Drilling Beyond Limits: Exploring the Depths of Directional Drilling
Understanding Directional Drilling
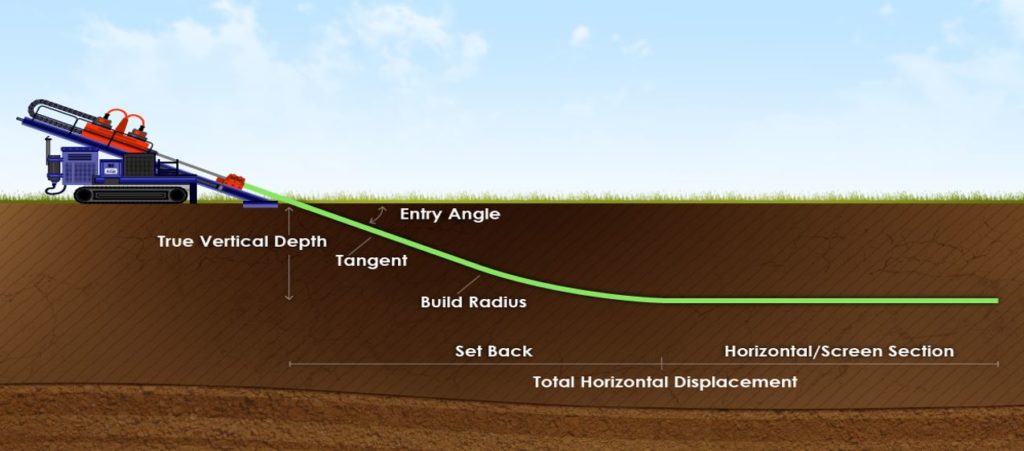
Directional drilling involves altering the trajectory of a wellbore to reach specific targets located horizontally or at angles from the vertical plane. This technique is employed to maximize reservoir exposure, increase productivity, and minimize environmental impact. It relies on advanced technologies such as rotary steerable systems, measurement while drilling (MWD), and logging while drilling (LWD) tools to provide real-time data for accurate wellbore positioning.

The Role of Rotary Steerable Systems
Rotary steerable systems (RSS) have emerged as a game-changer in directional drilling, offering greater control and efficiency compared to traditional motor assemblies. Unlike conventional drilling tools that rely on mud motors to steer the drill bit, RSS employs downhole mechanisms to adjust the wellbore trajectory while drilling, resulting in smoother curves and enhanced wellbore stability.
Utilizing Measurement While Drilling (MWD) and Logging While Drilling (LWD) Technologies
MWD and LWD technologies play a pivotal role in directional drilling operations by providing crucial data on wellbore inclination, azimuth, formation properties, and drilling parameters in real time. This enables engineers to make informed decisions on steering the wellbore towards its target while mitigating drilling risks such as deviation and collision with adjacent wells.
Applications of Directional Drilling
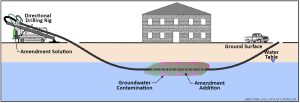
The versatility of directional drilling has led to its widespread adoption across various industries beyond oil and gas exploration. In the environmental sector, directional drilling is utilized for installing underground utilities, such as water and sewer lines, without disrupting surface infrastructure or environmentally sensitive areas. Additionally, directional drilling is employed in geothermal energy projects to access deep-seated heat reservoirs for sustainable power generation.
Enhancing Oil and Gas Recovery
Directional drilling plays a vital role in enhancing oil and gas recovery from mature reservoirs by accessing untapped reserves and maximizing reservoir contact. By drilling multiple lateral wells from a single vertical wellbore, operators can efficiently drain hydrocarbons from expansive reservoirs, thereby optimizing production rates and extending the economic life of the field.
Unlocking Unconventional Resources
The advent of directional drilling techniques has facilitated the exploitation of unconventional resources such as shale gas and tight oil formations. Horizontal drilling combined with hydraulic fracturing enables operators to access hydrocarbons trapped within low-permeability reservoirs, unlocking vast reserves that were previously considered uneconomical to produce.
Challenges and Innovations
Despite its myriad benefits, directional drilling presents unique challenges that necessitate ongoing innovation and technological advancements. Maintaining wellbore integrity, controlling drilling-induced vibrations, and accurately predicting formation characteristics are among the key challenges faced by engineers in directional drilling operations. To address these challenges, industry stakeholders are investing in research and development initiatives aimed at enhancing drilling efficiency, reducing costs, and minimizing environmental footprint.
Advancements in Drilling Automation
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms is revolutionizing drilling operations by automating decision-making processes and optimizing drilling parameters in real time. AI-powered drilling systems analyze vast datasets from previous drilling operations to identify patterns, predict drilling outcomes, and recommend optimal drilling strategies, thereby improving efficiency and reducing non-productive time.
Next-generation Drilling Tools and Materials
Continual advancements in drilling tools and materials are enhancing the performance and reliability of directional drilling operations. From advanced drill bits with improved cutting structures to high-strength materials capable of withstanding extreme downhole conditions, these innovations are enabling operators to drill deeper, faster, and more accurately than ever before.
The Future of Directional Drilling
As global energy demand continues to rise and conventional reserves become increasingly depleted, directional drilling will play an indispensable role in accessing and extracting hydrocarbons from challenging environments. With ongoing technological advancements and a growing emphasis on sustainability, the future of directional drilling holds promise for unlocking new reserves, maximizing resource recovery, and shaping the energy landscape for generations to come.
In conclusion, directional drilling represents a paradigm shift in the oil and gas industry, offering unprecedented opportunities for exploration and production in previously inaccessible regions. With its ability to navigate through complex geological formations and unlock unconventional resources, directional drilling is poised to remain a cornerstone of the energy industry’s quest for innovation and sustainability.